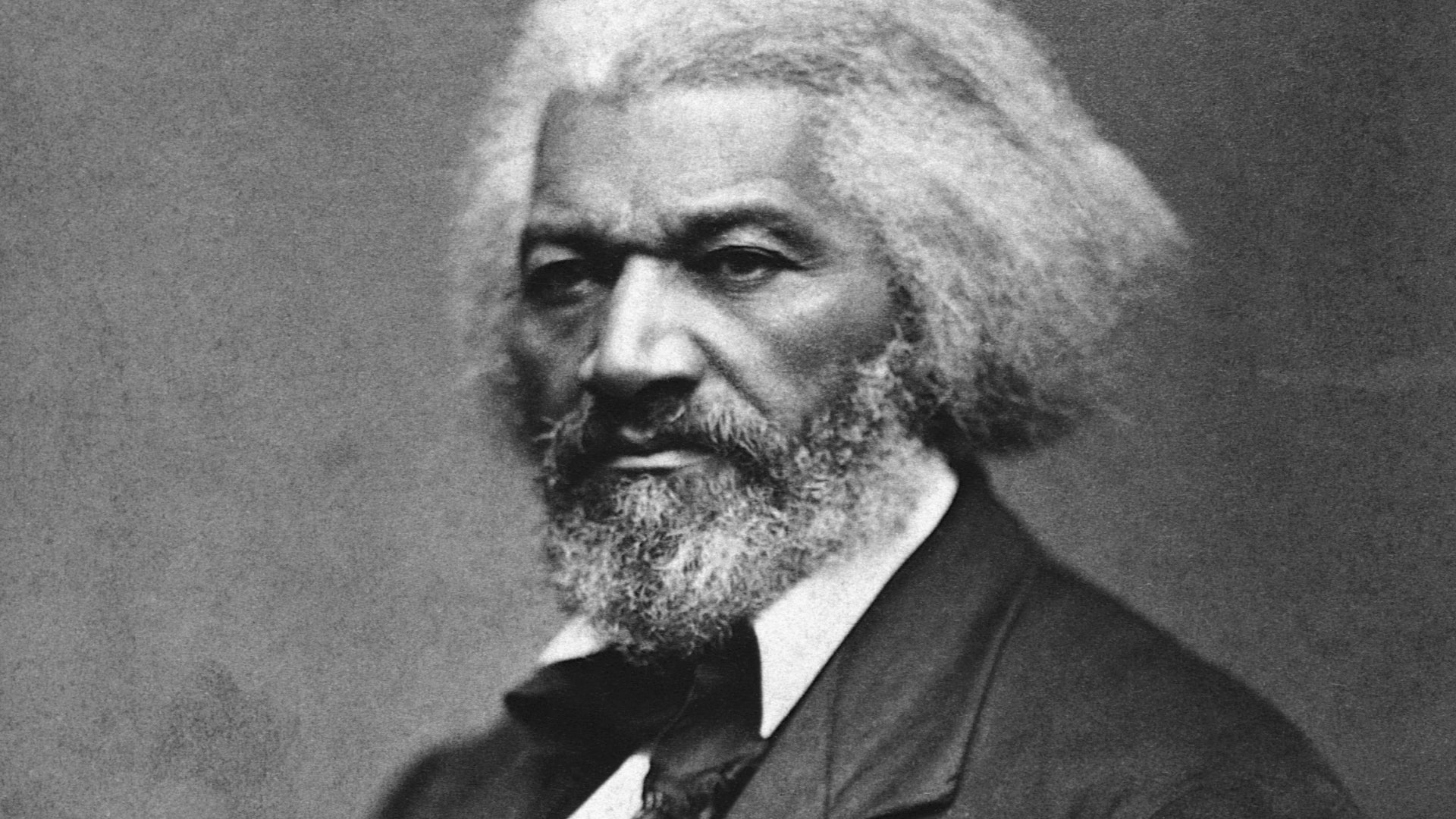Teaching Activity. By Ursula Wolfe-Rocca.
Students discover “echoes of enslavement” in their own state — discrete sites of remembering, forgetting, honoring, lying, or distorting — in this lesson based on the book How the Word Is Passed by Clint Smith.
Continue reading
Picture book. By Kelly Starling Lyons. 2012. 32 pages.
Story about a young girl during Reconstruction whose parents are finally able to have a legal marriage while honoring a family wedding tradition.
Continue reading
Book — Non-fiction. By Arisa White and Laura Atkins. 2019. 112 pages.
An illustrated children's book tells the story of real-life champion for civil rights Bridget "Biddy" Mason.
Continue reading
Book — Non-fiction. By Erica Armstrong Dunbar. 2019. 176 pages.
This book blends traditional biography with illustrations, photos, and engaging sidebars that illuminate the life of Harriet Tubman.
Continue reading
Teaching Activity. By Bill Bigelow, Adam Sanchez, and Ursula Wolfe-Rocca. Article by Adam Sanchez. 2022. Rethinking Schools
A role play about the demise of Reconstruction that helps students get beyond the question “Was Reconstruction a success or failure?”
Teaching Activity by By Adam Sanchez, Illustrator: Nate Kitch
Continue reading
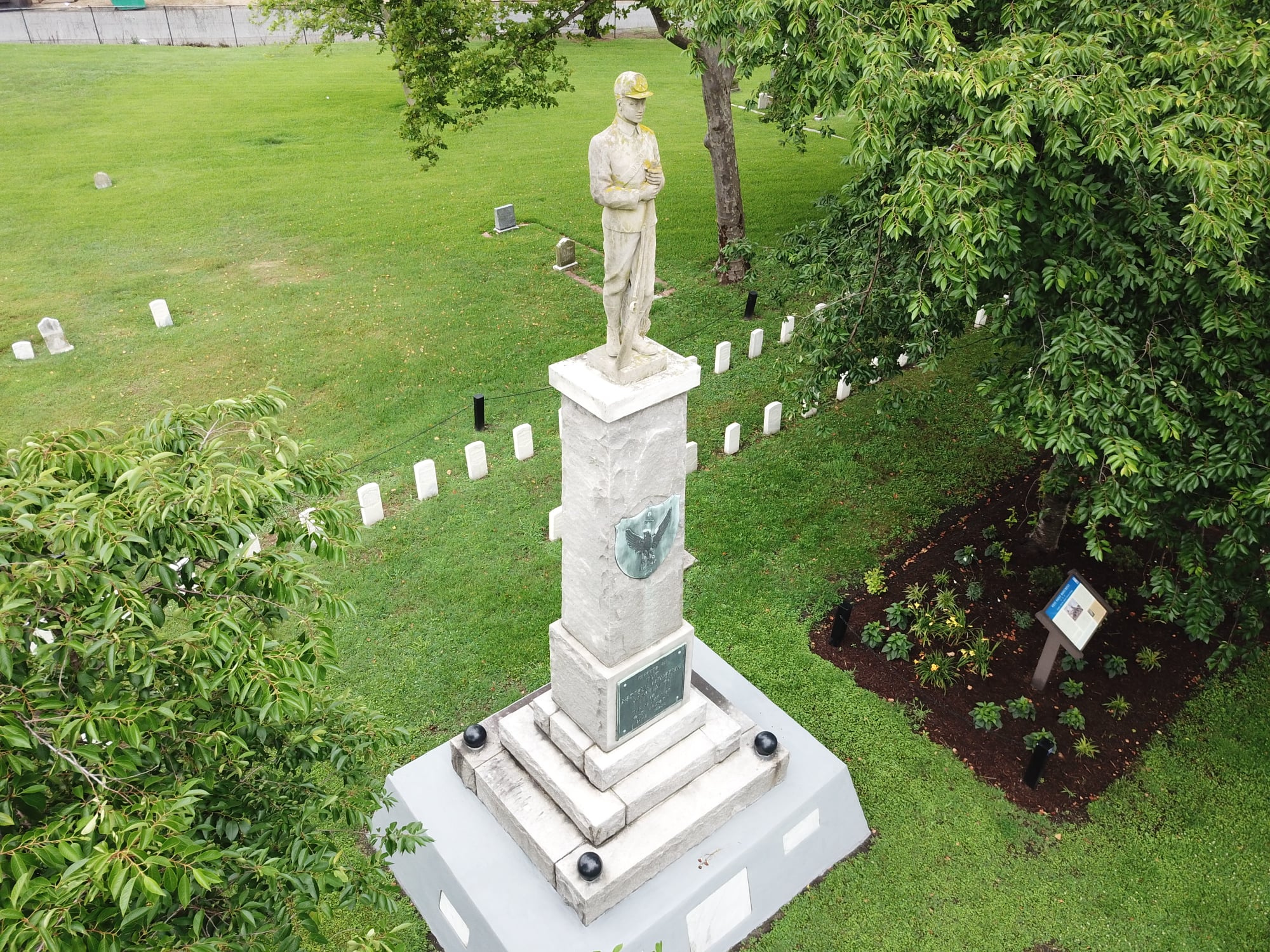
The West Point Cemetery in Norfolk, Virginia was established to provide a burial area for Black soldiers and sailors who fought to preserve the Union.
Continue reading
The Carroll County Courthouse Massacre left 23 Black people dead when an armed white mob attacked an ongoing trial.
Continue reading
Henry E. Hayne was the first Black student to be accepted to the University of South Carolina’s medical school, a bold act which encouraged other Black students to apply. By 1875, Black men comprised the majority of the student body.
Continue reading
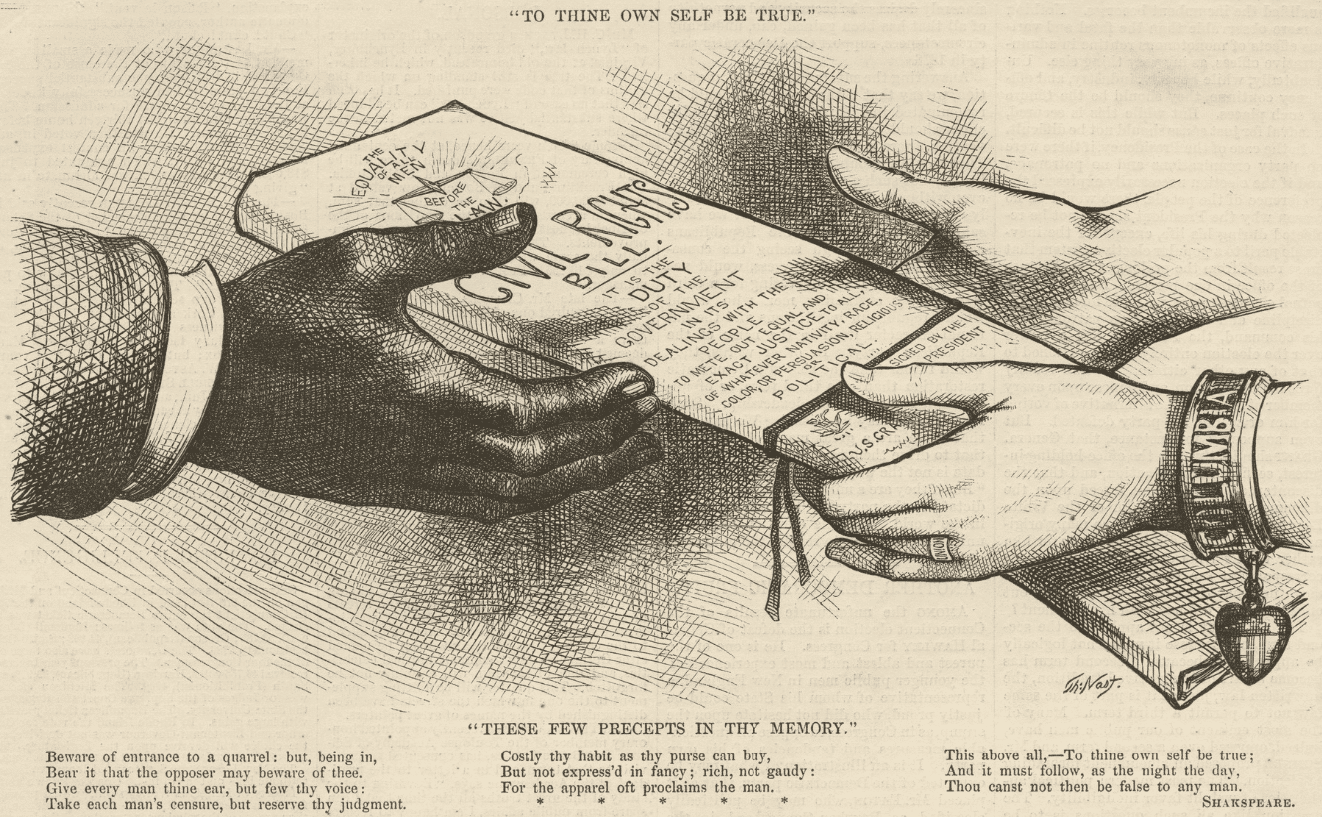
The U.S. Supreme Court ruled that the Civil Rights Act of 1875, forbidding discrimination in hotels, trains, and other public spaces, was unconstitutional and not authorized by the 13th or 14th Amendments of the Constitution.
Continue reading
During Reconstruction, Delaware’s Convention of Colored People gathered in Dover to discuss and demand state provisions to educate their children.
Continue reading
Elias Thomson, an African American who lived in Spartanburg, South Carolina, bravely shared testimony detailing violence inflicted against him because he voted for the Republican ticket in the local election.
Continue reading
In this speech, Frederick Douglass denounced the Civil Rights Cases of 1883, in which the Supreme Court held that the Thirteenth and Fourteenth Amendments did not empower Congress to outlaw racial discrimination by private individuals.
Continue reading
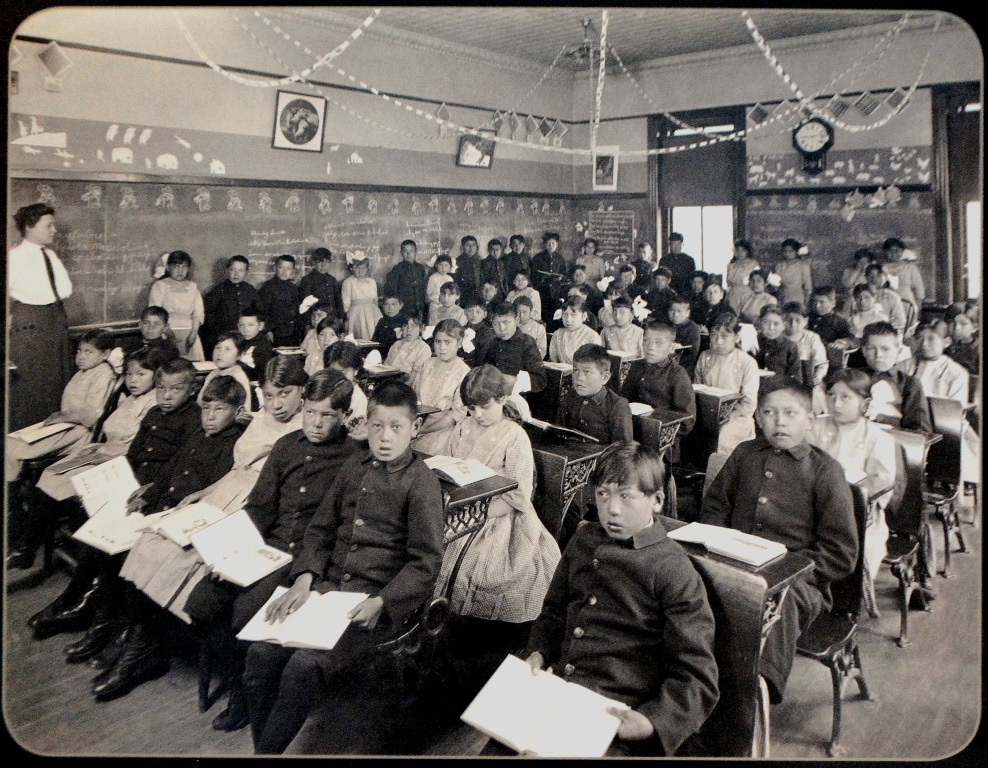
The Indian Industrial School of Genoa, Nebraska, the fourth non-reservation boarding school, was established by the Office of Indian Affairs.
Continue reading
Julius Taylor founded and ran Broad Ax, a Utah-based Black newspaper which challenged commonly accepted beliefs about politics and religion at the end of the twentieth century.
Continue reading
Along the “Trail of Tears” in Neligh, Nebraska, a farmer signed a deed to return ancestral land to the Ponca Tribe.
Continue reading
The Real Estate and Homestead Association helped organize travel and settlement for African Americans, “Exodusters,” who fled the South because of racial violence and “bulldozing” by white supremacist groups.
Continue reading
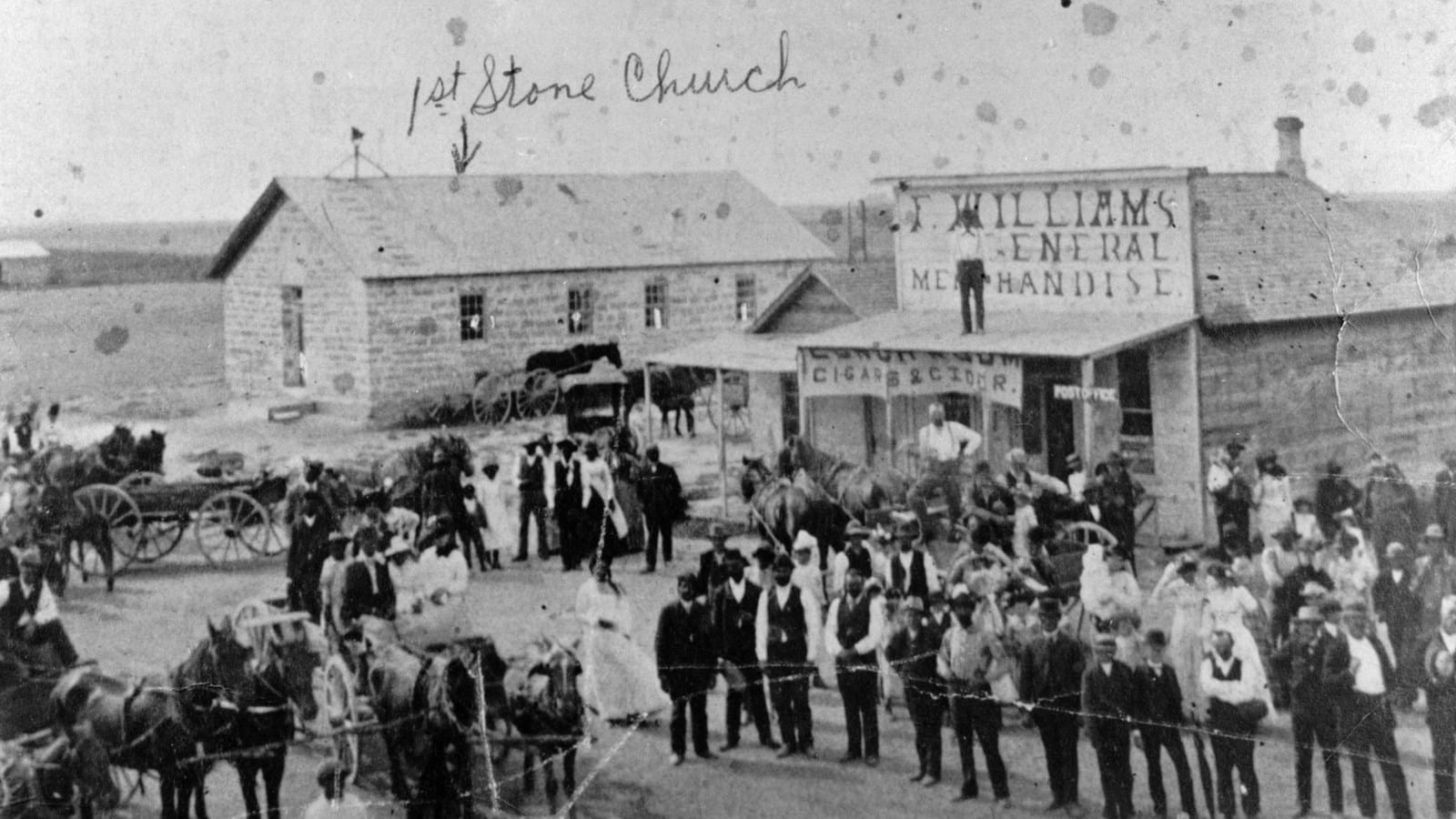
Six Black Kansans and a white developer created the Nicodemus Town Company. With the goal of establishing an all-Black settlement on the Great Plains, W. H. Smith and W. R. Hill advertised the town as a haven for Black migrants.
Continue reading
Book — Non-fiction. By Kidada E. Williams. 2024. 384 pages.
An account of the brutal white supremacist violence and terror that formerly enslaved people were faced with during Reconstruction.
Continue reading
Book — Non-fiction. By E. James West. 2022. 328 pages.
This biography examines the life of historian and activist Lerone Bennett Jr. and his influence on African American culture and history.
Continue reading
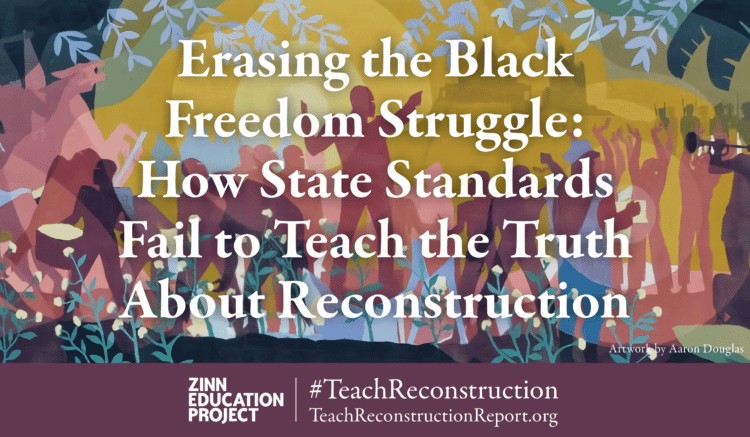
This month we released a printed edition of our national report, Erasing the Black Freedom Struggle: How State Standards Fail to Teach the Truth About Reconstruction. Thanks to the generous support of a donor, we can mail copies of the report to teacher educators, state and school district policymakers, and staff at historical societies.
Continue reading
Check out three stories about teachers who teach outside the textbook and organize to defend the right to teach people’s history.
Continue reading
Princeville, North Carolina originated as a resettlement community for freed people and became the oldest incorporated city chartered by African Americans in the United States.
Continue reading
Book — Non-fiction. By Thulani Davis. 2022. 464 pages.
The author traces how people newly freed from bondage created political organizations and connections that mobilized communities across the South during Reconstruction, building on a long tradition of organizing against all odds.
Teaching Activity by Thulani Davis
Continue reading
Teaching Activity. By Mimi Eisen and Ursula Wolfe-Rocca. 47 pages.
A follow-up lesson to “Reconstructing the South,” using primary source documents to reveal key outcomes of the Reconstruction era.
Continue reading
Book — Non-fiction. By Gerald Horne. 2022. 632 pages.
A detailed history of counterrevolutionary forces in Texas state history.
Continue reading