An employee of the U.S. Senate, Kate Brown found political support from Sen. Charles Sumner and others in Congress when she was violently removed from the ladies' car, which was segregated illegally.
Continue reading
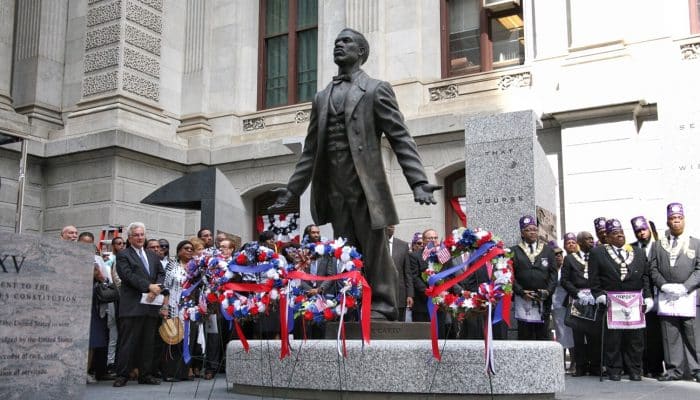
President Ulysses S. Grant signed into law the third of the Enforcement Acts, a Reconstruction-era bill that empowered the federal government to intervene when the 13th, 14th, and 15th Amendments are violated.
Continue reading
Book — Non-fiction. By W. E. B. Du Bois. Edited by Eric Foner and Henry Louis Gates. 2021. 1097 pages.
Originally published in 1935, Du Bois’ Black Reconstruction was the first book to challenge the prevailing racist historical narrative of the era and in sharp, incisive prose, tell the story of the Civil War and Reconstruction from the perspective of African Americans.
Continue reading
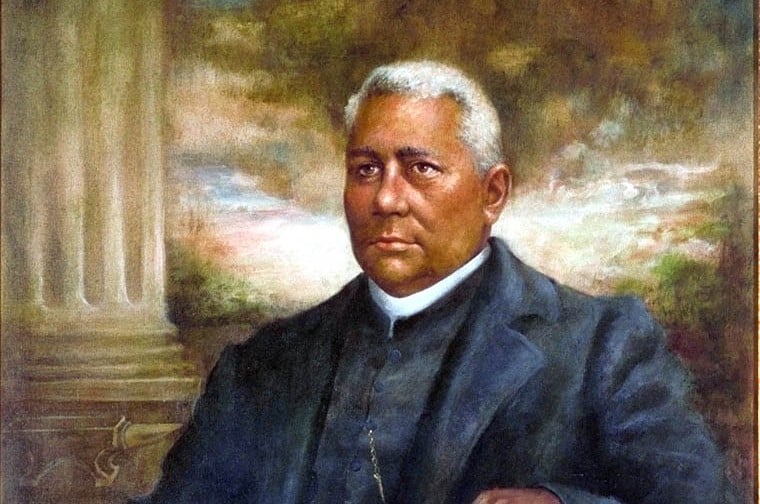
Henry McNeal Turner addressed the Georgia Legislature on its decision to expel all Black representatives.
Continue reading
The South Carolina Constitutional Convention convened to disenfranchise Black voters.
Continue reading
F. M. B. “Marsh” Cook, a white man, was killed for standing up against the white supremacist 1890 Mississippi Constitutional Convention.
Continue reading
As African Americans marched peacefully in response to their expulsion from elected office, more than a dozen were massacred near Albany, Georgia.
Continue reading
The New Orleans Massacre occurred when white residents attacked Black marchers near the reconvened Louisiana Constitutional Convention.
Continue reading
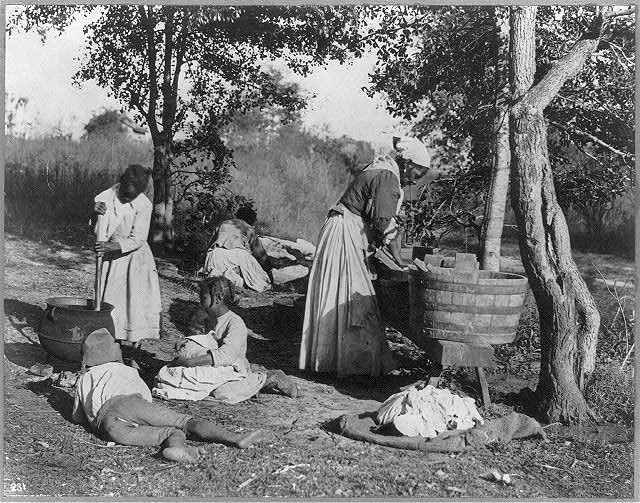
Black women in Atlanta who washed clothes for a living organized an effective Reconstruction era strike — with clear demands, strategic timing, and door-to-door canvassing.
Continue reading
Teaching ideas and discussion questions for How the Word Is Passed: A Reckoning with the History of Slavery Across America by Clint Smith.
Continue reading
Book — Non-fiction. By Brandy Colbert. 2021. 216 pages.
History of Oklahoma including Trail of Tears, Reconstruction, Black towns, Red Summer, Jim Crow, Black and white newspapers, lynchings, Tulsa Race Massacre, and the ongoing fight for reparations and historical memory.
Continue reading
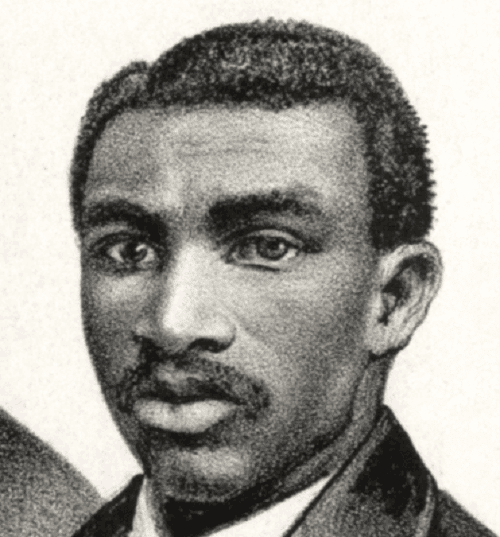
Philadelphia, Pennsylvania Black educator, baseball player, and civil rights activist Octavius V. Catto was murdered by a white supremacist on election day.
Continue reading
Teaching Guide. By American Social History Project with foreword by Eric Foner. 1996.
Primary documents, essays, and questions to teach the untold story of Reconstruction.
Continue reading
The St. Bernard Parish massacre of African Americans was carried out by white men to terrorize the recently emancipated voters in Louisiana.
Continue reading
For the first time, African Americans were elected to the House of Representatives in 1870.
Continue reading
Book — Non-fiction. Edited by Kinshasha Holman Conwill and Paul Gardullo. 2021. 224 pages.
Essays on the history and legacy of Reconstruction, a companion to the Smithsonian’s National Museum of African American History and Culture exhibit.
Continue reading
Book — Fiction. By Howard Fast. 1944. 294 pages.
The politics and economics of Reconstruction told through memorable historical fiction.
Continue reading
Picture book. By Chris Barton. Illustrated by Don Tate. 2015. 50 pages.
An in-depth look at the Reconstruction period through the life of one of the first African-American congressmen.
Continue reading
Delegates gathered in Montgomery, Alabama, to draft a new state constitution during Reconstruction.
Continue reading
Robert Smalls was elected to Congress from South Carolina during Reconstruction.
Continue reading
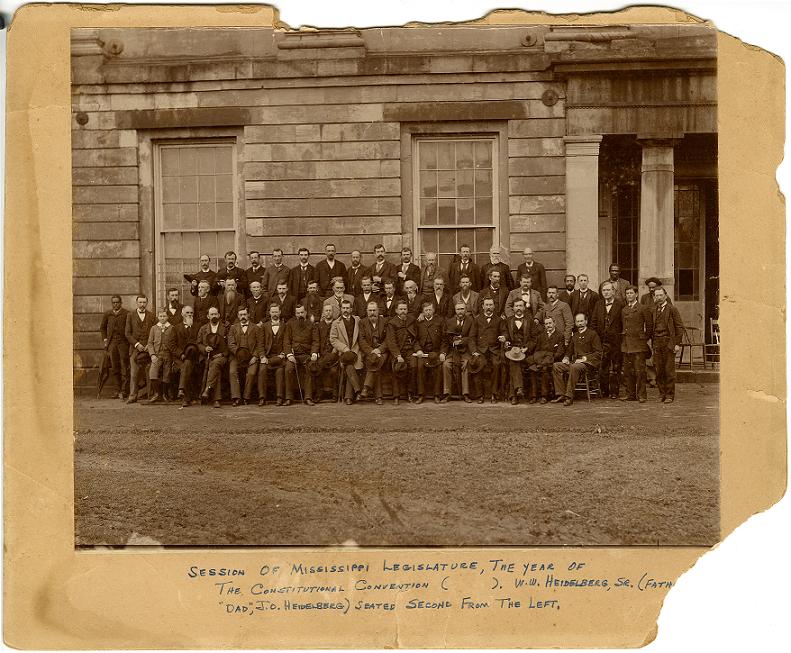
Mississippi adopted a state constitution with poll tax and literacy tests to roll back the gains of the Reconstruction era.
Continue reading
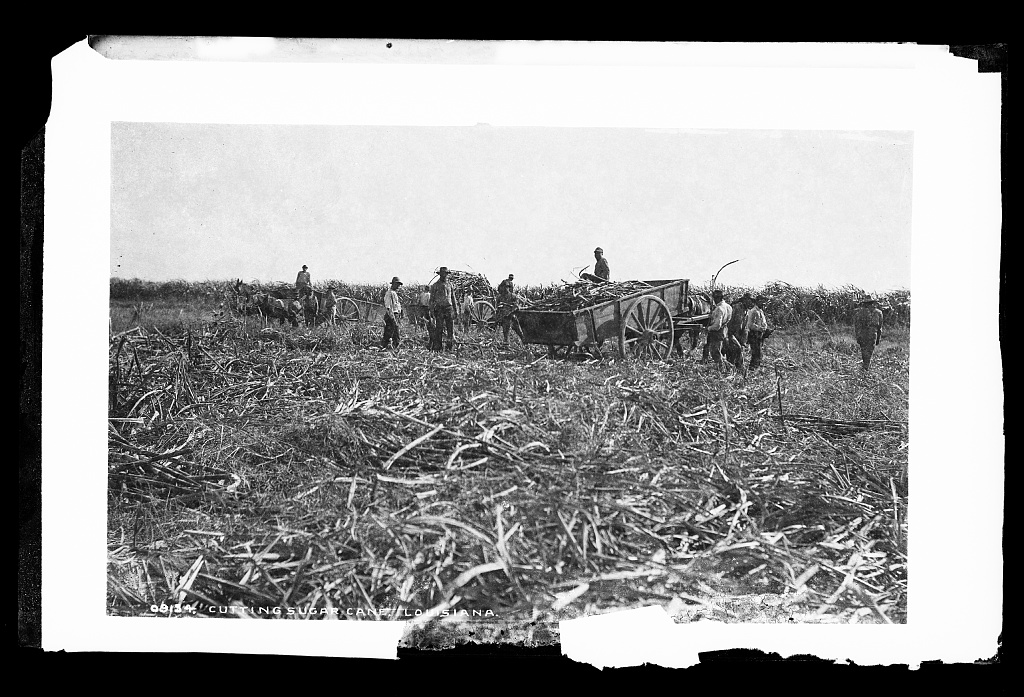
Between 30-60 striking Black Louisiana sugarcane workers were massacred.
Continue reading
Teaching Guide. Edited by Adam Sanchez. 2019. Rethinking Schools. 181 pages.
Students will discover the real abolition story, one about some of the most significant grassroots social movements in U.S. history.
Continue reading
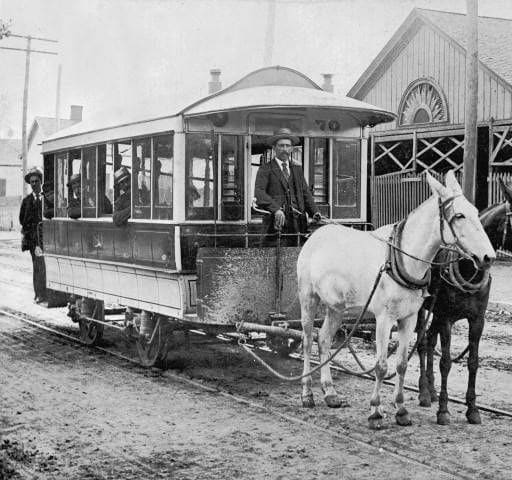
Reconstruction era protest of racist discrimination on streetcars in Louisville, Kentucky.
Continue reading
The 13th Amendment to the U.S. Constitution officially ended the institution of slavery.
Continue reading