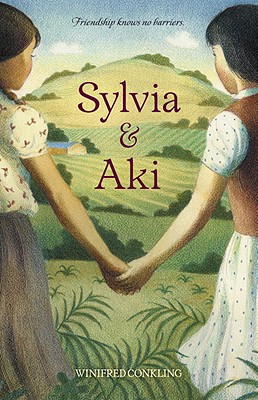Teaching Activity. By Bill Bigelow. Rethinking Schools. 7 pages.
A companion lesson to the Eyes on the Prize segment on school desegregation.
Continue reading
Picture book. By Duncan Tonatiuh. 2014. 40 pages.
Upper elementary school picture-book about the Mendez v. Westminster case to desegregate California schools.
Continue reading
Teaching Activity. By Linda Christensen. Rethinking Schools. 21 pages.
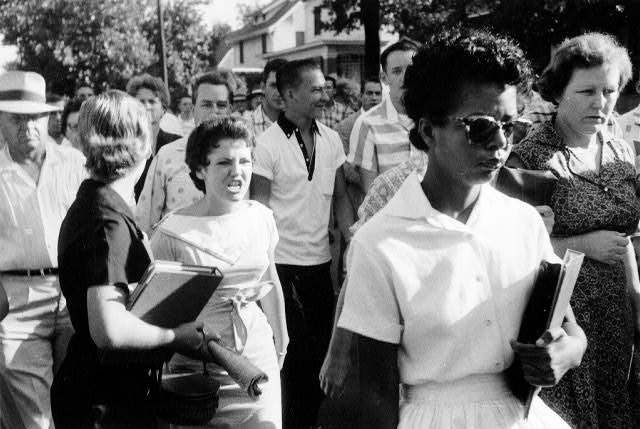
Role play and writing activities for language arts and social studies on Brown v. Board and the Little Rock Nine. Designed for use with the memoir Warriors Don’t Cry.
Continue reading
Book — Historical fiction. By Winifred Conkling. 2011. 160 pages.
Based on the true story of two girls who meet in 1940s California and a landmark lawsuit on education.
Continue reading
Film. By William Elwood. 1990. 56 minutes.
The little known story of Charles Hamilton Houston who paved the road to Brown v. Board.
Continue reading
Book — Non-fiction. By John A. Stokes with Lois Wolfe. 2007. 128 pages.
First person description of the student led movement to desegregate schools in Prince Edward County.
Continue reading
Book — Non-fiction. By Philippa Strum. 2010. 186 pages.
Description of a pre-Brown v. Board desegregation court case involving Mexican-American families.
Continue reading
Book — Non-fiction. By Richard Kluger. 2004. 880 pages.
One of the first texts, now a classic, on Brown v. Board of Education.
Teaching Activity by Richard Kluger
Continue reading
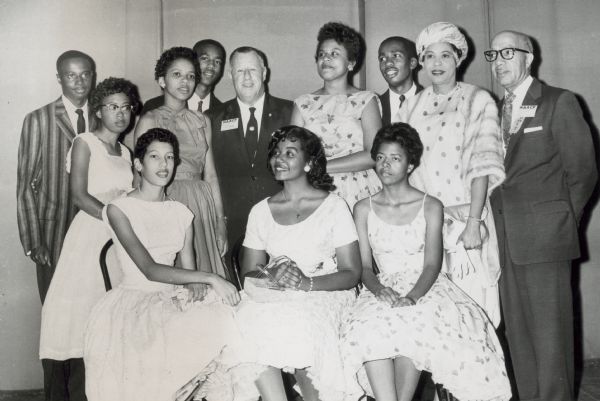
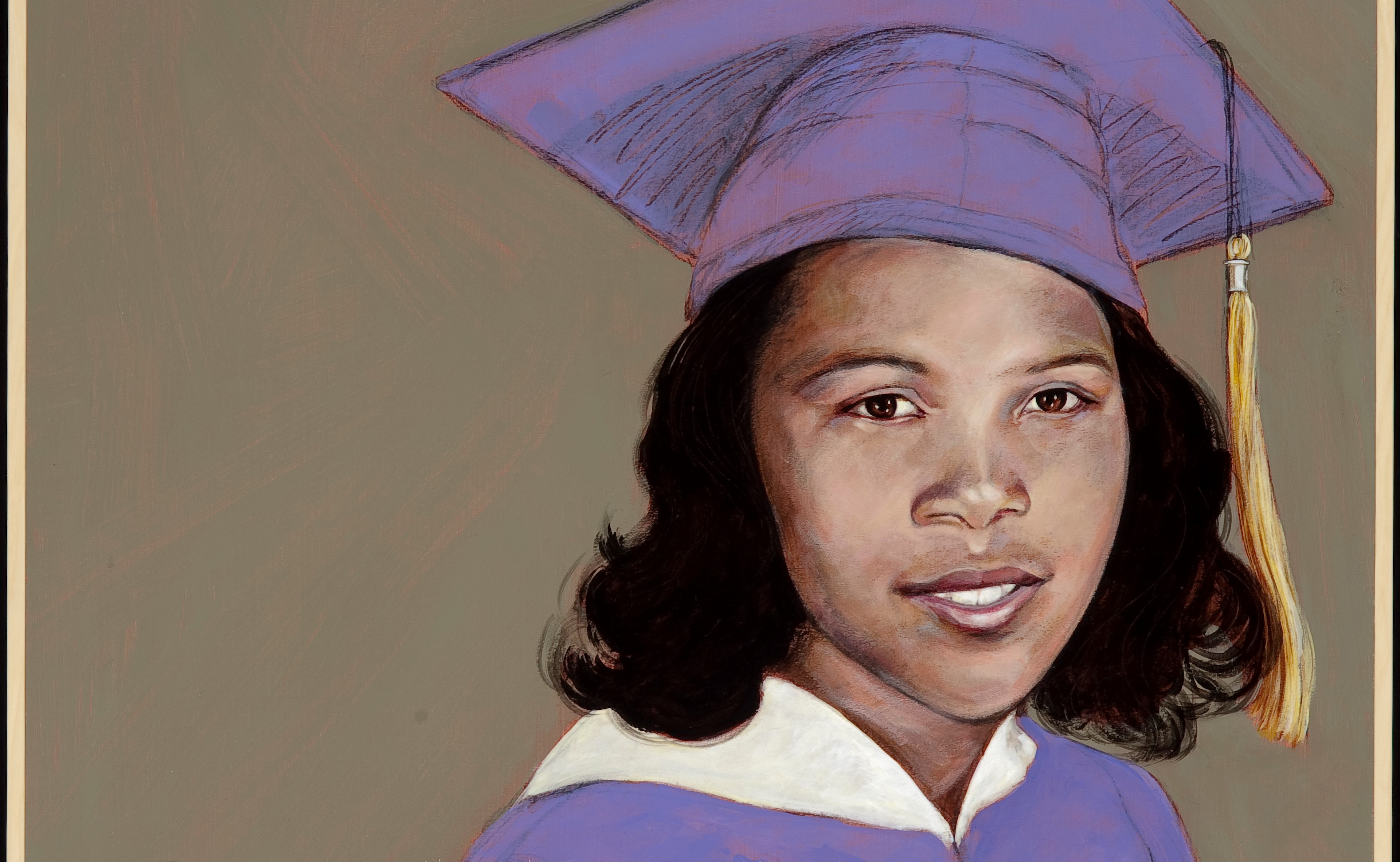
Book — Non-fiction. By Melba Pattillo Beals. 2007. 336 pages.
Story of a teenage girl chosen to integrate Little Rock High School.
Continue reading
Teaching Guide and Website. Edited by Deborah Menkart, Alana D. Murray, and Jenice L. View. 2024. 390 pages.
This second edition provides lessons and articles for K–12 educators on how to go beyond a heroes approach to the Civil Rights Movement, with a focus on education, economics, labor, youth, women, and culture.
Continue reading
Book — Fiction. By Toni Morrison. 2004. 80 pages.
Fictional story and real photographs tell the story of desegregation, for upper elementary and above.
Continue reading
The Supreme Court ruled that schools in the U.S. had to desegregate “immediately,” instead of the previous ruling of “with all deliberate speed.”
Continue reading
More than 450,000 New York City school children boycotted school as part of a protest for quality schools for Black and Latino students.
Continue reading
The Chicago Public School Boycott, also known as Freedom Day, was a mass boycott and demonstration against the segregationist policies.
Continue reading
26,000 high school and college students came to Washington, D.C. to demand the end of segregated schools.
Continue reading
A. Philip Randolph, Jackie Robinson, Coretta Scott King, Harry Belafonte, Bayard Rustin, and more led a Youth March for Integrated Schools in Washington, D.C.
Continue reading
The U.S. District Court for the Southern District of Texas Corpus Christi found a South Texas school district guilty of discriminating against Mexican-American students in one of the first cases that directly applied the ruling made in Brown v. Board of Education to Mexican-American students.
Continue reading
In an effort to stop the implementation of Brown v. Board through terrorism, 16-yr-old John Earl Reese was killed in Mayflower, Texas.
Continue reading
Barbara Johns (16-years-old) led her classmates in a strike to protest the substandard conditions in Prince Edward County, Virginia.
Continue reading
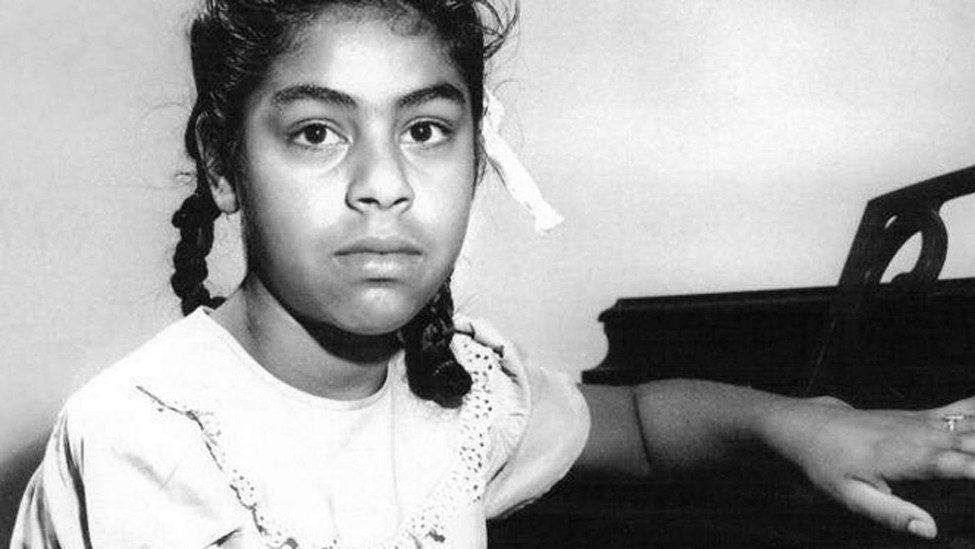
When Gonzalo and Felicitas Mendez, two California farmers, sent their children to a local school, their children were told that they would have to go to a separate facility reserved for Mexican American students.
Continue reading
The courts ruled in favor of the Mendez family and their co-plaintiffs in California, finding segregated schools to be unconstitutional.
Continue reading
On Flag Day 1943, the Supreme Court invalidated a compulsory flag salute law in public schools and established that students possess some level of First Amendment rights.
Continue reading
The U.S. Supreme Court ruled that, in the case of nine-year old Chinese-American Martha Lum, her exclusion on account of race from school was justified.
Continue reading
The Michigan Supreme Court ruled in favor of school desegregation in the case of Joseph Workman v. the Detroit Board of Education, almost 90 years before the United States’ landmark Brown v. Board of Education.
Continue reading