A meeting was held in New York of abolitionists to address the injustice of continued slavery in Cuba.
Continue reading
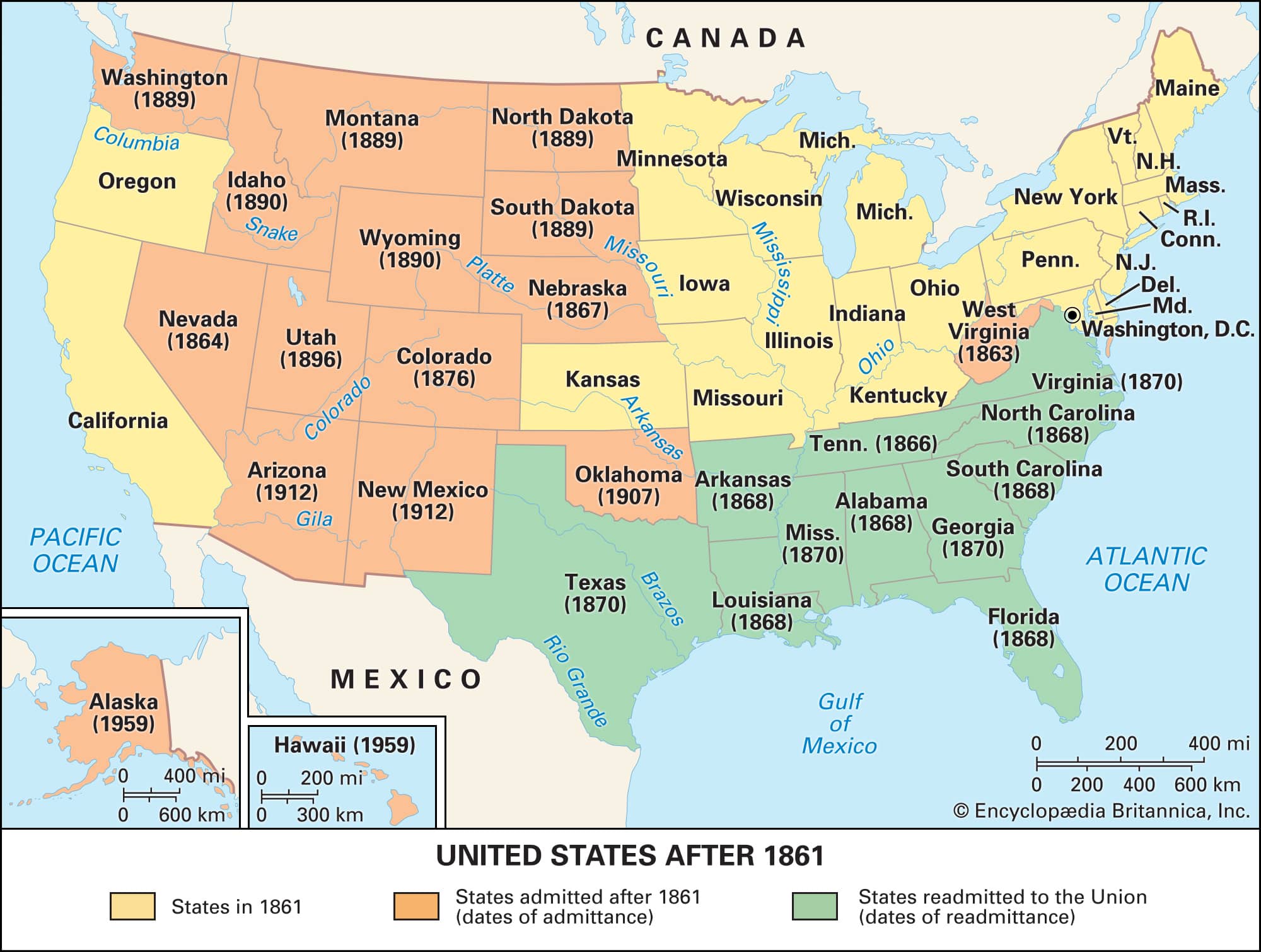
Congress overrode President Andrew Johnson’s veto and passed the first of four statutes known as the Reconstruction Acts, which outlined the process of readmission to the Union.
Continue reading
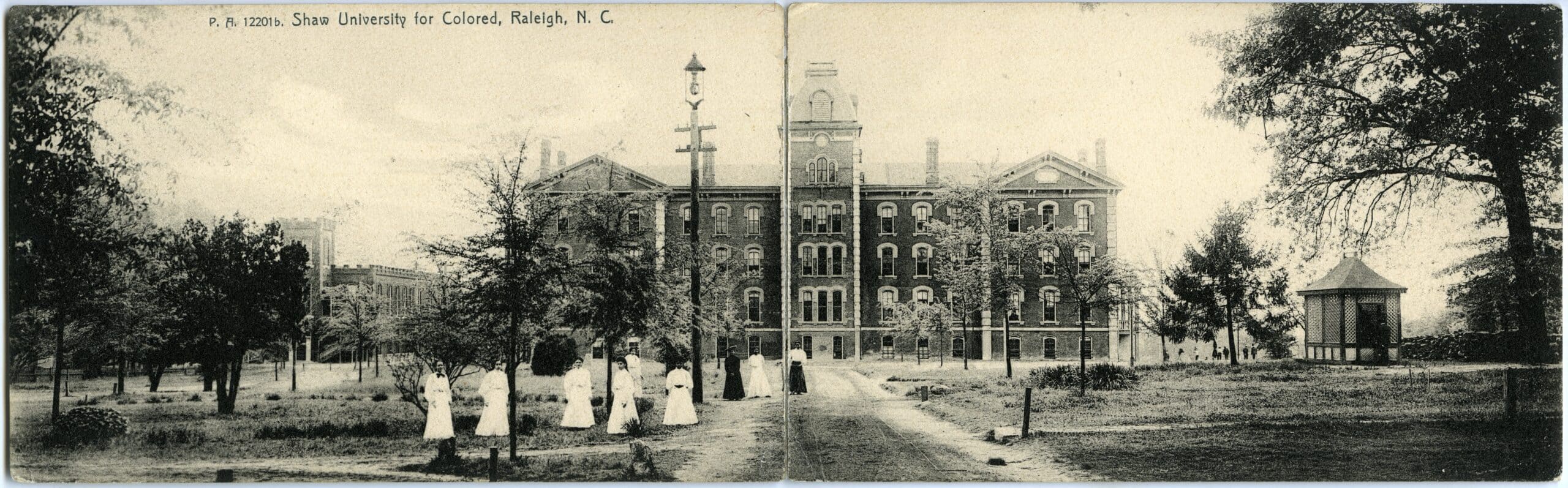
Shaw University was established as a co-ed campus with support from private donors and the Bureau of Refugees, Freedmen and Abandoned Lands. It is the second oldest HBCU in the South.
Continue reading
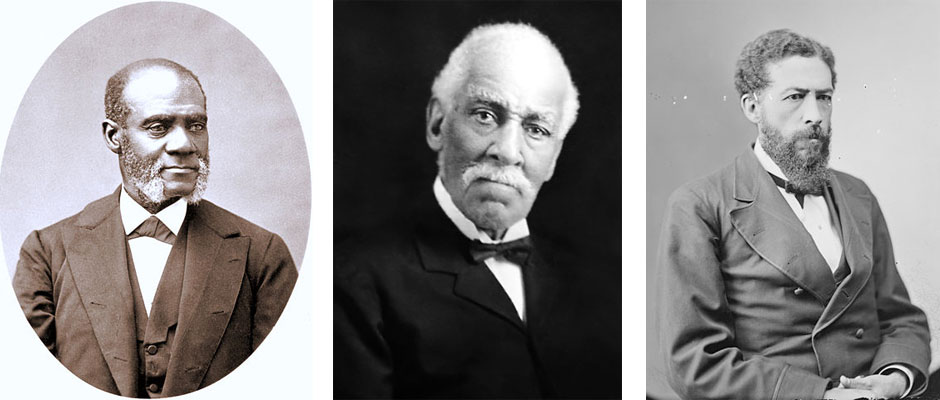
Tunis Campbell, who assisted in the Port Royal Experiment to assist freed people during Reconstruction, was an abolitionist, state senator, and justice of the peace.
Continue reading
The Union Army occupied the Sea Islands off the coast of South Carolina, freeing approximately 10,000 people who had been enslaved, starting what became known as the Port Royal Experiment.
Continue reading
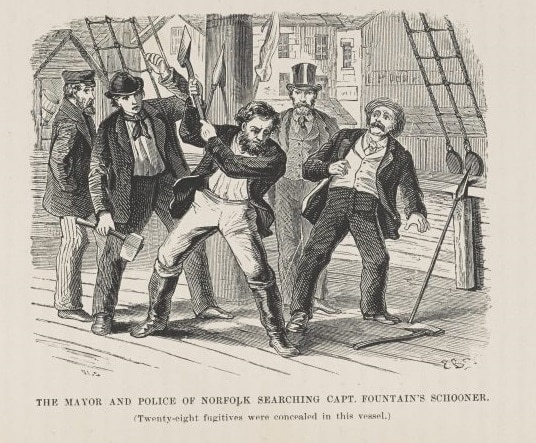
With escalating escapes of the formerly enslaved, the Virginia General Assembly responded to lobbying from slaveholders and human traffickers by making it harder for enslaved African Americans to escape on ships and by increasing penalties for anyone helping such freedom-seekers.
Continue reading
Abolitionists freed a man captured under the Fugitive Slave Act of 1850 in Syracuse, New York.
Continue reading
A Boston judge stopped the extradition of George Latimer, who had escaped enslavement in Virginia, and allowed him to raise funds for his own manumission.
Continue reading
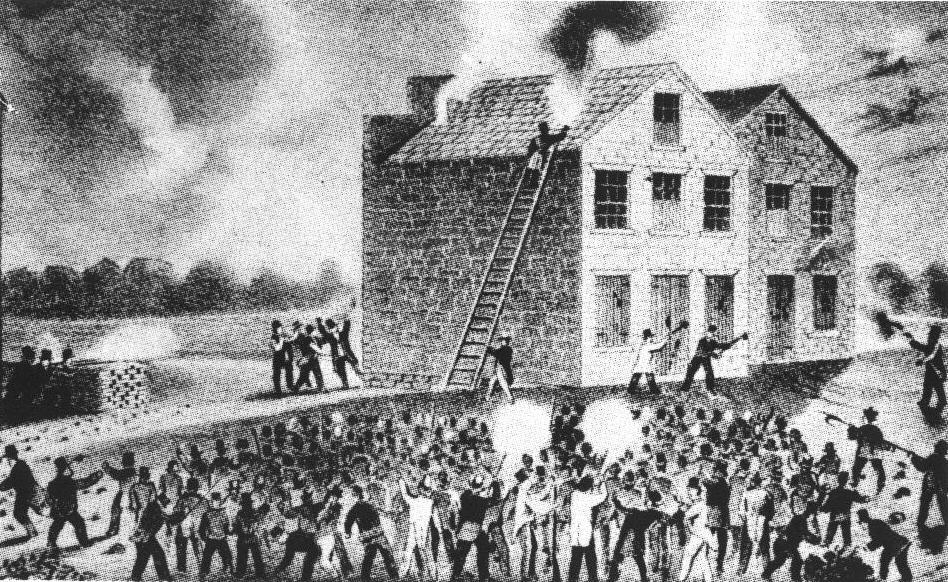
Minister, journalist, newspaper editor, and abolitionist Elijah Parish Lovejoy was murdered by a pro-slavery mob.
Continue reading
Freedom’s Journal was the first African American owned and operated newspaper in the United States.
Continue reading
Born on this day in Massachusetts, Charles Sumner was outspoken against slavery, for full recognition of Haiti, against the U.S.-Mexico War, for true reconstruction with land distribution, against school segregation, and much more.
Continue reading
A group of African Americans presented a petition for freedom to the Massachusetts Council and the House of Representatives.
Continue reading
Approximately ninety-six Africans held captive on the British slave ship Little George revolted against the ship’s captain and crew, eventually taking control of the entire ship.
Continue reading